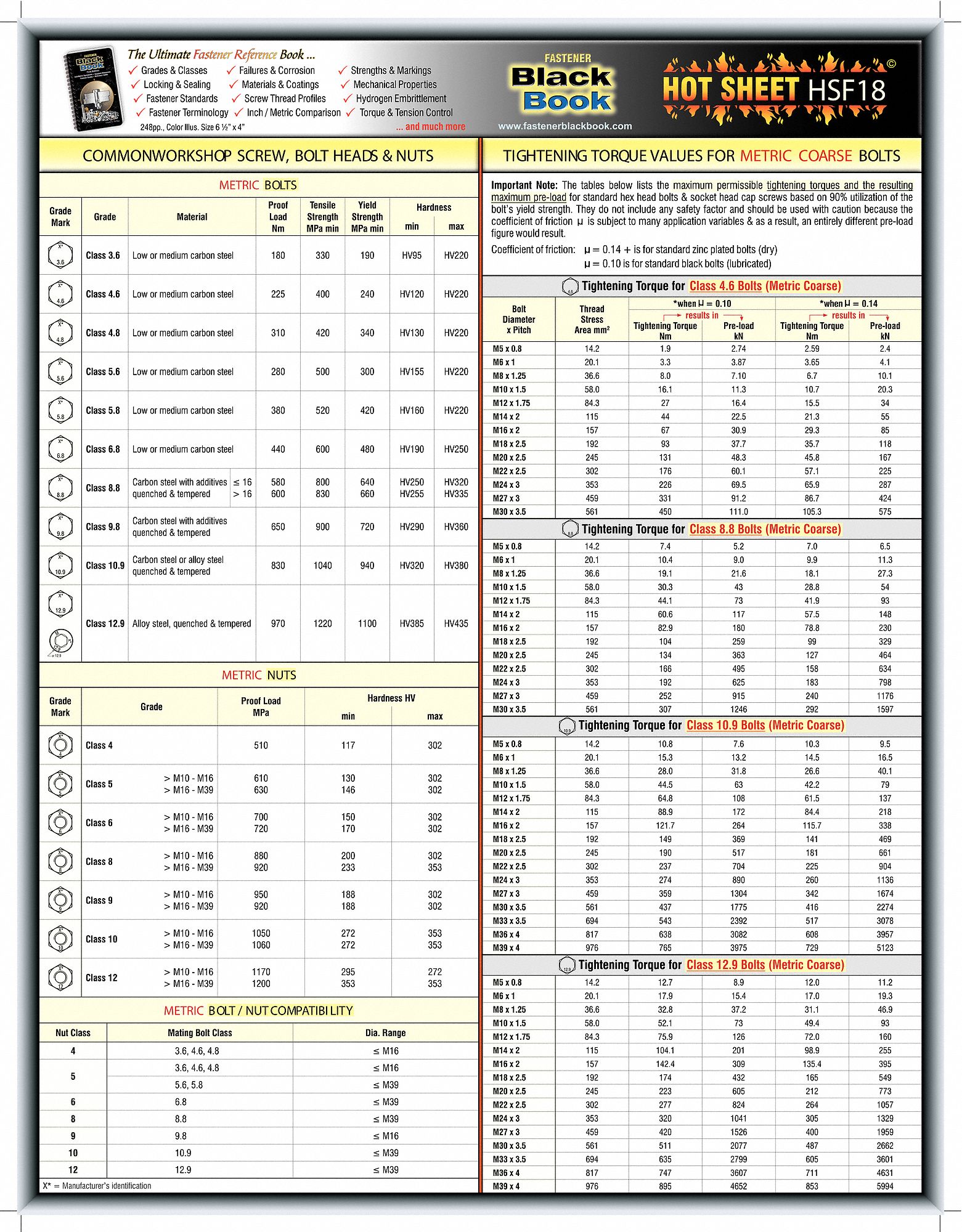
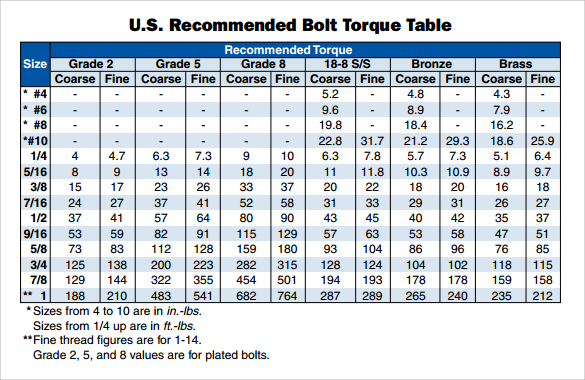
Securing components effectively is crucial in any assembly, especially when working with aluminum, a lightweight yet strong material common in various industries. Understanding the appropriate tightening force, guided by a metric bolt torque specification, is paramount for achieving a reliable and durable joint. Improper torquing can lead to stripped threads, weakened joints, or even component failure. This guide delves into the intricacies of applying correct metric bolt torque when fastening into aluminum.
Using a correct metric bolt torque value ensures the clamping force required to hold components together securely without over-tightening. Over-torquing can damage the aluminum threads, making the joint weaker and potentially leading to failure. Conversely, under-torquing can result in a loose joint, compromising the structural integrity of the assembly. Therefore, adhering to recommended torque specifications is essential for optimal performance and safety.
While general torque charts provide a starting point, factors like thread size, bolt grade, and lubricant can influence the ideal torque. Consulting a specific metric bolt torque chart tailored for aluminum applications is crucial for achieving the correct clamping force. These specialized charts often incorporate factors specific to aluminum, like its softer nature compared to steel.
Historically, torque specifications have evolved alongside advancements in material science and fastening technology. As engineers gained a deeper understanding of stress distribution and material properties, more precise torque recommendations emerged. Early practices relied on experience and rule-of-thumb methods, which were often inconsistent and unreliable. The development of standardized torque charts, particularly those addressing specific material combinations like metric bolts in aluminum, represents a significant improvement in fastening reliability.
The importance of a reliable metric bolt torque guideline when working with aluminum cannot be overstated. Aluminum's malleability requires careful attention to torque to avoid damage. Over-tightening can easily strip threads, while under-tightening can lead to joint loosening and potential component failure, especially under vibration or stress. Utilizing accurate torque values ensures the integrity of the assembly and prevents costly repairs or replacements.
Torque is the rotational force applied to a fastener, measured in Newton-meters (Nm). A metric bolt torque chart for aluminum provides the recommended Nm values for different bolt sizes and grades. For instance, an M6 stainless steel bolt into aluminum might have a recommended torque of 10 Nm. Using a calibrated torque wrench helps achieve this precise value.
One benefit of using a metric bolt torque chart for aluminum is preventing thread damage. Another advantage is achieving consistent clamping force, which ensures uniform load distribution and prevents joint failure. Finally, proper torque application maximizes the lifespan of the assembled components by minimizing stress and wear.
For accurate torque application, start by cleaning the bolt threads and the aluminum mating surface. Then, apply the appropriate lubricant as recommended in the chart. Select the correct torque wrench and set it to the specified Nm value based on the bolt size and grade. Tighten the bolt smoothly and steadily until the wrench clicks, indicating the target torque has been reached. Avoid jerky movements or over-tightening.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Torque Chart
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Prevents thread damage | Chart selection can be complex |
| Ensures consistent clamping force | Requires calibrated tools |
| Maximizes component lifespan | Environmental factors can influence torque |
Best practices include using a calibrated torque wrench, cleaning threads, applying lubricant, tightening smoothly, and regularly checking torque values. Challenges include variations in aluminum alloys, differing thread conditions, and environmental factors like temperature. Solutions involve using specific torque charts, inspecting threads, and controlling environmental conditions.
Frequently asked questions often revolve around correct torque values for different bolt sizes, the importance of lubrication, and the types of torque wrenches to use. Answers generally point to consulting specific charts, using appropriate lubricants, and employing calibrated torque wrenches.
Tips include using a torque chart specific to the aluminum alloy and bolt material, regularly calibrating torque wrenches, and avoiding excessive force. Tricks can involve using thread locking compounds to prevent loosening in high-vibration environments.
In conclusion, understanding and applying the correct metric bolt torque when fastening into aluminum is fundamental for achieving strong and reliable joints. Using a specific metric bolt torque chart tailored to aluminum, following best practices, and understanding potential challenges contribute to successful assembly. By mastering these principles, you can prevent costly repairs, ensure component longevity, and maintain the structural integrity of your aluminum assemblies. Consulting relevant engineering standards and manufacturer guidelines further enhances your understanding and application of proper torque techniques. This proactive approach will ultimately save time, resources, and contribute to a safer and more reliable final product. Take the time to select the correct chart and tools, and always prioritize accurate torque application for optimal results.
Frank knight property listings hot right now
Magical girl raising project chapter 40 insights
Unlocking potential with malone solutions in louisville ky